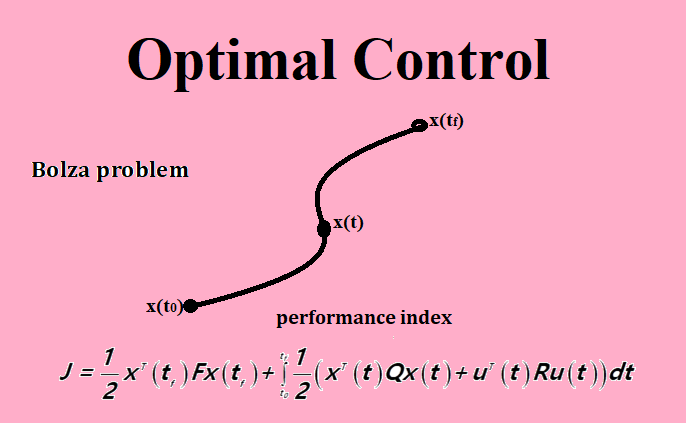
The main objective of optimal control is to determine control signals that will cause a process (plant) to satisfy some physical constraints and at the same time extremize (maximize or minimize) a chosen performance criterion (performance index or cost function).
The course will give Master 1 Automatic and Systems students an introduction to the basic concepts of optimization and control of dynamic systems, emphasizing mathematical techniques such as calculating variations and solving differential equations and integrals of higher degree.
The course aims to provide a fundamental understanding of the main results in optimal control.
At the end of the course, the student should be able to:
- Use the calculus of variations to solve different optimization problems,
- Adapt the steps leading up to the Euler-Lagrange equation to account for different boundary conditions,
- Explain the main steps in the proof of Pontryagin’s Maximum Principle (PMP),
- Use PMP to solve optimal control problems,
- Solve Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) problems,
- Explain the bang-bang principle in optimal control,
- Explain the principles behind the most standard algorithms for the numerical solution of optimal control problems and use Matlab to solve these problems.
- Teacher: abbadi amel